What if the key to a more sustainable future lies in the ground beneath our feet? Building long-term soil fertility is key in permaculture. It focuses on creating a regenerative ecosystem that boosts soil health and biodiversity. By using sustainable agriculture and regenerative farming, we can improve soil fertility. This reduces the need for outside help and makes ecosystems more resilient.
Permaculture teaches us to learn by observing and thinking about ecological systems. This is vital for permaculture soil ecology and sustainable farming. By understanding soil, plants, and microorganisms, we can design better agricultural systems. These systems promote soil health and biodiversity, leading to more productive and sustainable ecosystems.
Key Takeaways
- Building long-term soil fertility is a cornerstone of permaculture, focusing on creating a sustainable and regenerative ecosystem through permaculture soil ecology.
- Permaculture principles encourage redundancy in important functions, such as water conservation and soil formation, which is critical for sustainable agriculture practices.
- Soil built in temperate climates can result in creating approximately 3 times more soil than in tropical climates, highlighting the importance of regenerative farming methods.
- Increased organic matter in soil helps maintain soil moisture, reducing the need for external inputs and promoting soil health through permaculture soil ecology.
- Permaculture design methodology teaches us to think through the cycles, functions, structures, and dynamic principles of ecological systems, which is essential for implementing sustainable agriculture practices and regenerative farming methods.
- By adopting permaculture principles, farmers and gardeners can enhance soil fertility, reduce the need for external inputs, and create more resilient ecosystems, ultimately leading to more productive and sustainable ecosystems through regenerative farming methods.
Understanding Permaculture Soil Fertility
Permaculture soil fertility comes from a diverse group of microorganisms. These tiny creatures are key to breaking down organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and making minerals available. By supporting these microorganisms, permaculture helps keep the soil fertile and the ecosystem healthy. This method uses organic soil management and holistic land management techniques.
For example, adding leaf mold helps the soil hold more water. Using biochar also makes nutrients more accessible. These steps are crucial for a healthy soil environment.
Some important ecological gardening techniques in permaculture include rotational grazing. This method boosts soil life by breaking down organic matter. It also uses beneficial fungi to fight off diseases and improve soil health. These methods help create a strong, sustainable ecosystem.
The advantages of permaculture soil management are clear. It improves water retention, boosts biodiversity, and enhances nutrient cycling. By using these practices, people can cut down on chemical fertilizers and pesticides. This leads to a healthier ecosystem and less pollution.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotational grazing | Increases microbiological activity |
| Beneficial fungi | Out-competes disease organisms and enhances soil biology |
| Leaf mold addition | Increases water retention |
The Importance of Soil Tests
Soil tests are key in permaculture. They help check soil health and find ways to improve it. By knowing how soil, plants, and tiny life forms interact, farmers can boost soil biodiversity enhancement, follow natural farming principles, and fix ecosystems. A small soil sample, about 1 cup, can show a lot about a big area’s soil.
Testing soil pH is very important. It affects how well plants get nutrients. Phosphorus and potassium are needed in big amounts for plants to grow well. For more on DIY soil testing, check out soil testing resources. They explain why soil tests are crucial for understanding soil life.

Choosing the Right Soil Test
It’s important to pick the right soil test. Think about the plants you’re growing and what they need. Some tests check for harmful elements, which is good for older homes because of lead.
Interpreting Soil Test Results
Understanding soil test results is complex. It involves knowing how soil, plants, and tiny life forms work together. The Soil Analyst Cooperative offers tools to make sense of these results and suggest organic fixes. By using soil tests, permaculture farmers can make their ecosystems better. This helps their farms stay healthy for a long time and cuts down on chemical use.
Techniques for Enhancing Soil Health
Regenerative farming methods like composting and mulching are key to better soil health. They improve soil structure and boost organic matter. These practices also support good microorganisms. By using holistic land management, farmers can help ecosystems, cut down on erosion, and improve water quality.
Organic soil management is vital for keeping soil fertile and diverse. It uses natural materials like compost and manure to enrich the soil. By cutting down on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, farmers can make a healthier place for their crops and the ecosystem around them.
Composting for Nutrient-Rich Soil
Composting is a simple way to make soil rich in nutrients. It breaks down organic stuff like food waste and leaves into a nutrient-rich humus. This humus can be added to the soil. It makes the soil better at holding water, supports beneficial microorganisms, and improves soil structure.
Mulching to Retain Moisture
Mulching is another way to improve soil health. It involves covering the soil with organic stuff like straw or wood chips. Mulching keeps moisture in, fights weeds, and controls soil temperature. It helps farmers use less water and makes farming more sustainable.
- Improved soil structure and fertility
- Increased organic matter and biodiversity
- Reduced erosion and water pollution
- Enhanced ecosystem services and resilience
By using regenerative farming and organic soil management, farmers can make farming more sustainable and productive. Holistic land management is crucial for better ecosystem services, less environmental harm, and food security for the long term.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Composting | Improves soil structure, increases organic matter, and supports beneficial microorganisms |
| Mulching | Retains moisture, suppresses weeds, and regulates soil temperature |
| Regenerative farming methods | Improves soil fertility, reduces erosion, and promotes ecosystem services |
The Role of Cover Crops
Permaculture soil ecology depends a lot on cover crops. They help make the soil fertile and support sustainable farming. By using cover crops, farmers can make their farms more diverse and strong. This method focuses on keeping the soil healthy and full of life.
Permaculture cover crops help in many ways. They can fix nitrogen, improve soil structure, or keep pests away. This makes the soil better for growing plants.

Using different types of cover crops boosts soil diversity. This helps many tiny life forms in the soil. The cover crops also protect the soil from harsh weather and pests. This makes the soil healthier.
By using these methods, farmers can use less chemical fertilizers. This makes farming more sustainable.
Benefits Beyond Nutrient Fixation
Cover crops do more than just fix nutrients. They provide homes for good insects and attract bees. They also help control weeds and diseases, reducing the need for chemicals.
They also stop soil from washing away and keep moisture in the soil. This is very helpful for plants.
Types of Cover Crops for Permaculture
There are many cover crop mixes for different times of the year. For spring and summer, an oat/pea mix works well. In the fall and winter, a mix with rye and vegetables is good.
In places with mild winters, a mix of favas, vetch, and wheat or rye is common. Choosing the right cover crops helps farmers build a strong and sustainable farm.
Using Organic Matter to Build Soil
Organic matter is key in organic soil management. It makes soil better, holds more water, and helps good microbes grow. About 50% of soil organic matter comes from microbes.
In holistic land management, organic matter is vital for healthy soils. You can get it from compost, manure, green manure, and cover crops. To add it to soil, you can compost, mulch, or use cover crops as green manure.
Adding organic matter boosts soil health a lot. It makes nutrients available to plants, supports many soil organisms, and helps water soak in better. A study showed that plant roots release substances that help make soil organic matter. But, it’s hard to measure because it changes with plant types and conditions.
- Increased biomass production
- Using cover crops to raise organic matter and contribute to soil nutrient levels
- Conservation agriculture principles to increase organic matter deposition and carbon sequestration
By using these methods, farmers and gardeners can make their soil healthier. This leads to more crops and better soil life. Research shows that adding animal manure or carbon-rich waste can greatly increase soil organic matter. This makes the soil healthier and more structured.
| Practice | Effect on Organic Matter |
|---|---|
| Increased biomass production | Significant boost to organic matter levels |
| Conservation agriculture principles | Increase in organic matter deposition and carbon sequestration |
| Use of cover crops | Contribution to soil nutrient levels and increase in organic matter |
Biodiversity and Soil Fertility
Soil biodiversity is key in permaculture for a healthy ecosystem. It helps grow good microorganisms. By using natural farming and ecological gardening, we can make soil better, grow more food, and use less outside help.
It’s important to know how soil biodiversity works. We can do this by mixing different plants together. This helps them all grow better.
How Biodiversity Improves Soil Health
Soil life includes bacteria, fungi, insects, and more. These are vital for soil health. Microorganisms break down organic matter and recycle nutrients.
Using natural farming and ecological gardening boosts soil life. This makes soil more fertile and better structured.
Companion Planting Strategies
Companion planting is about putting different plants together. It helps soil health, grows more food, and cuts down on outside help. This method makes ecosystems more diverse and strong.

Biodiversity in soil has many benefits. It makes soil more fertile, grows more food, and makes ecosystems stronger. By using natural farming and ecological gardening, we can make our ecosystems more sustainable and productive.
| Soil Type | Characteristics | Sustainable Cultivation Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soils | Low in nutrients | Organic matter addition |
| Silty Soils | Well-drained and nutrient-rich | Minimal tillage |
| Clay Soils | Dense and fertile | Organic matter addition and mulching |
Permaculture Practices for Soil Building
Permaculture design is key to creating sustainable ecosystems. It uses regenerative farming methods to improve soil health and biodiversity. This method focuses on renewable resources, minimal waste, and biodiversity.
Good organic soil management keeps soil fertile and structured. Cover crops, compost, and mulch help a lot. Also, holistic land management practices, like smart water use, save water, reduce erosion, and boost soil health.
- Observe and interact with nature to foster sustainable decision-making
- Use renewable resources and reduce reliance on non-renewable sources
- Promote biodiversity and enhance resilience within agricultural systems
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Earth care | Protect and preserve the natural environment |
| People care | Promote social justice and human well-being |
| Future care | Ensure the long-term sustainability of ecosystems and communities |
By following these principles and practices, we can make ecosystems more resilient and productive. This way, we also reduce our environmental impact.
Soil Erosion and Conservation
Soil erosion is a big problem for our ecosystems. It hurts the health of the soil and makes our ecosystems less strong. To stop soil erosion, we can use natural farming ways. This includes planting cover crops, mulching, and making terraces.
These methods slow down water and spread it out on slopes. This helps prevent soil erosion.
Studies show that contouring can cut soil erosion by 50%. Planting different types of plants can reduce erosion by about 30%. Also, a thick layer of mulch can soak up 70% of raindrop impact. This stops soil from getting compacted and eroded.
Swales can increase water soaking into the soil by nearly 40%. This helps manage water during heavy rains.
Some good ways to stop soil erosion are:
- Planting deep-rooted plants to hold soil and keep water
- Making terraces to lessen erosion on steep slopes
- Using a thick layer of mulch to catch raindrop impact
By using these methods, permaculture experts can help keep soil safe. This also helps our ecosystems stay strong and diverse. It makes our ecosystems more sustainable and resilient.
| Technique | Erosion Reduction |
|---|---|
| Contouring | 50% |
| Diversifying plant life | 30% |
| Mulching | 70% (raindrop impact absorption) |
The Impact of Soil pH
Soil pH is key to keeping soil fertile. It affects how nutrients are available and how microorganisms work. In permaculture, knowing soil pH is vital for good soil management. Most plants like a pH between 6.5 and 7.5. Some can handle a wider range, from 5.5 to 8.
For sustainable farming, soil microbes like a pH close to neutral (pH 7.0). Healthy soil has about 50 billion microbes in just 1 tablespoon. This shows how important it is to create a good home for these microbes. Using organic matter helps keep the soil pH balanced.
Understanding Soil pH Levels
Soil pH shows how acidic or alkaline the soil is. Lowering the pH by one point makes it 10 times more acidic. Two points make it 100 times more acidic. This highlights the need to manage soil pH carefully to keep the balance of microbes.
Amending Soil pH for Fertility
To change soil pH, you can use organic or inorganic materials. For example, sulphur can lower pH. You need 49 g to 146 g per square meter, depending on the pH you want. Sphagnum peat moss is another option, with 2.5-5 cm added to the top 20-30 cm of soil before planting.
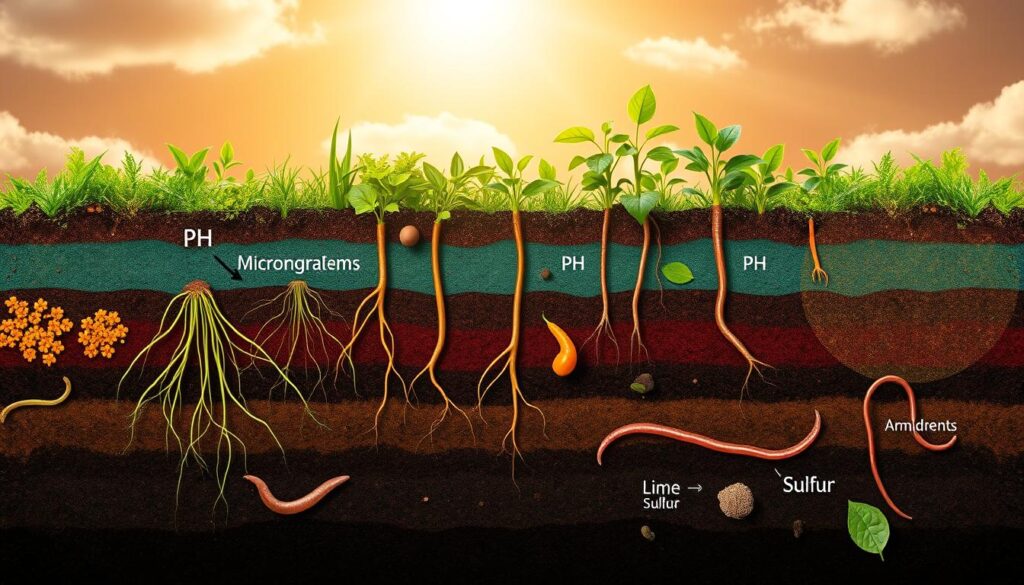
Managing soil pH helps make soil more fertile. It also boosts crop yields and supports ecosystem health. This is crucial in permaculture, where the goal is a balanced and sustainable ecosystem.
| pH Level | Soil Condition |
|---|---|
| 6.5-7.5 | Neutral |
| 5.5-6.5 | Slightly acidic |
| 7.5-8.0 | Slightly alkaline |
The Role of Mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae are crucial for soil health, working with plant roots to get nutrients. This partnership is key for organic soil management and holistic land management. It boosts soil biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Some key benefits of mycorrhizae include:
- Improved nutrient uptake and exchange between plants and soil
- Enhanced soil structure and water retention
- Increased resistance to diseases and pests
To help mycorrhizae grow, we can use methods like minimal tillage and cover cropping. Adding organic amendments also helps. These actions boost soil biodiversity enhancement and make the soil better for mycorrhizae.

By supporting mycorrhizal growth, permaculture helps soil become more fertile and plants healthier. This is vital for keeping ecosystems strong. It follows the rules of organic soil management and holistic land management.
| Benefits of Mycorrhizae | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Nutrient Uptake | Mycorrhizae increase the surface area of plant roots, allowing for better nutrient absorption |
| Enhanced Soil Structure | Mycorrhizae help to aggregate soil particles, improving soil structure and water retention |
| Increased Disease Resistance | Mycorrhizae can produce compounds that help to protect plants from diseases and pests |
Nutrient Cycling in Permaculture
Nutrient cycling is key in permaculture. It moves nutrients around the ecosystem. By using composting and cover crops, farmers can cut down on outside help and make soil better.
Organic soil care, like mulching and using animals, is also important. It helps nutrients move around. This way, nutrients stay in the system, not lost.
Permaculture aims for closed nutrient loops. This boosts soil health and makes ecosystems stronger. Recycling nutrients, like using urine or animal manure, is part of this.
Good water management is also crucial. It helps spread nutrients evenly. This reduces waste and supports sustainable farming. Nutrient cycling is vital in permaculture, showing the need for balance in farming.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Composting | Transforming food waste into nutrient-rich compost |
| Cover Cropping | Planting crops to retain soil nutrients and prevent erosion |
| Integrating Livestock | Using animal manure to enrich the soil and promote nutrient cycling |
Utilizing Animal Manure
Animal manure is a valuable resource in permaculture. It provides natural nutrients for soil. In permaculture, using animal manure is key for sustainable farming. It helps reduce waste and promotes nutrient cycling.
The benefits of using animal manure in permaculture are many. Different manures offer different advantages. For example:
- Chicken manure, which is high in nitrogen and phosphorus
- Cow manure, which is rich in organic matter and microorganisms
- Sheep manure, which is high in potassium and can help improve soil structure
It’s important to apply manure safely to avoid contamination. This means composting it to kill harmful organisms. Also, apply it at the right time and amount. Using animal manure helps reduce synthetic fertilizer use. It promotes a sustainable and ecological gardening approach.
Animal manure also improves soil structure and boosts biodiversity. By using manure, farmers create a more resilient ecosystem. It’s a key strategy for maintaining healthy soils and promoting ecological gardening.
| Type of Manure | Nutrient Content | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken Manure | High in nitrogen and phosphorus | Promotes healthy plant growth |
| Cow Manure | Rich in organic matter and microorganisms | Improves soil structure and fertility |
| Sheep Manure | High in potassium | Helps improve soil structure and increases crop yields |
The Benefits of Crop Rotations
Crop rotations are key in organic soil management. They boost soil fertility and cut down pests and diseases. By changing crops, farmers make nutrients more available and improve soil health. This method is vital for holistic land management, linking soil, plants, and microorganisms.
Studies show crop rotation greatly improves soil health. For instance, permaculture sites have 27% more soil carbon than control fields. This shows how important it is to enhance soil biodiversity for healthy soils.
Designing Effective Crop Rotations
To make good crop rotations, farmers must think about soil type, climate, and crop needs. They should plan a diverse rotation with crops like legumes, cereals, and root vegetables. This boosts soil biodiversity and lowers pest and disease risks.
Enhancing Nutrient Availability
Crop rotations also make nutrients more available. They help grow microorganisms that fix nitrogen and make phosphorus easier to use. Cover crops, like legumes, fix nitrogen and add organic matter. This reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and supports sustainable farming.
| Soil Health Indicator | Permaculture Sites | Control Fields |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Organic Carbon Content | 3.4 ± 0.3 g/100g | 2.0 ± 0.3 g/100g |
| Soil Bulk Density | 20% lower | – |
| Earthworm Abundance | 201% higher | – |
Natural Pest Management and Soil Health
Natural pest management is key in permaculture. It uses ecological gardening to control pests and keep ecosystems healthy. By following natural farming, we can cut down on external inputs, boost soil health, and build ecosystem strength. This is crucial for keeping soil fertile and supporting biodiversity.
Healthy soils are linked to pest control. They support beneficial microorganisms that help manage pests. Ecosystem restoration methods like companion planting and crop rotation can also help. For instance, African and Mexican Marigolds are great at keeping pests away from crops.
Some effective natural pest management strategies include:
- Companion planting: using pest-repellent species to deter pests
- Crop rotation: disrupting pest life cycles and minimizing damage to crops
- Biological control: using beneficial insects to control harmful pests
Permaculture focuses on sustainability. It uses ecological gardening, natural farming, and ecosystem restoration. This approach creates a balanced and strong ecosystem. It benefits the environment, produces healthy food, and supports the well-being of everyone involved.
Long-term Strategies for Sustaining Fertility
. At the heart of this endeavor lies the importance of
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
. Permaculture design methodology encourages students to hone their observational skills. It helps them develop the ability to think through the intricate cycles, functions, structures, and dynamic principles of ecological systems.
The Role of Community in Soil Health
cannot be overstated. By working together and sharing knowledge, permaculture practitioners can cultivate more effective strategies. These strategies help maintain soil fertility, improve ecosystem resilience, and promote regenerative farming methods.
This holistic approach to organic soil management empowers the creation of diverse, productive, and resilient ecosystems. These ecosystems support both human and environmental well-being.

